 There is nothing worse than turning up your music only to hear your car speakers or subwoofers rattle and buzz because they are damaged. Well, there is something worse: You could turn up the volume and hear nothing at all. We hear stories about people damaging their car speakers all the time. In almost every case, the issue is over-powering them because of unwise adjustments to the sound system. In this tongue-in-cheek article, we’ll discuss the five fastest ways to blow your car speakers. Let’s be clear: We don’t want you to damage your speakers and, more importantly, your hearing. The reality is, this is a list of five things NOT to do to your car stereo system. We hope you enjoy!
There is nothing worse than turning up your music only to hear your car speakers or subwoofers rattle and buzz because they are damaged. Well, there is something worse: You could turn up the volume and hear nothing at all. We hear stories about people damaging their car speakers all the time. In almost every case, the issue is over-powering them because of unwise adjustments to the sound system. In this tongue-in-cheek article, we’ll discuss the five fastest ways to blow your car speakers. Let’s be clear: We don’t want you to damage your speakers and, more importantly, your hearing. The reality is, this is a list of five things NOT to do to your car stereo system. We hope you enjoy!
1. Turn Up the Gains on Your Amps
 When a mobile electronics specialist installs an amplifier in your vehicle, the gain control (also called the sensitivity control) should be adjusted so that the amp will produce its maximum power when the volume on the source unit is turned up all the way. Some installers provide a little extra range on the volume so that quiet recordings can still play loudly. This is called gain overlap.
When a mobile electronics specialist installs an amplifier in your vehicle, the gain control (also called the sensitivity control) should be adjusted so that the amp will produce its maximum power when the volume on the source unit is turned up all the way. Some installers provide a little extra range on the volume so that quiet recordings can still play loudly. This is called gain overlap.
The amount of power your amplifier produces is fixed. That is to say, no amount of knob-turning, button-pushing or amp-gain-tweaking will allow it to produce more power. Turning up the gains on your amp only causes the amp to produce full power with a lower input voltage from your source unit. There is no benefit to this, and depending on your system, could introduce more background noise.
If you think your system doesn’t play loudly enough or seems to get too loud with only a little turn of the volume, go back to your installer and have him or her check the settings on the amp while playing the music you enjoy.
2. Crank the Bass Boost!
 Perhaps the most dangerous control on an amplifier, besides an improperly set gain control, is the bass boost control. In all cases, this single-band equalizer increases the output of the amplifier around a specific range of frequencies — usually in the 40 to 50 Hz region. What the control doesn’t do is increase the maximum available power from your amp. If your audio system is configured to produce full power with the volume on your radio turned up all the way, turning up the bass boost on an amp or processor will cause the amp to distort at the frequencies that you have boosted. It won’t make the system play any louder.
Perhaps the most dangerous control on an amplifier, besides an improperly set gain control, is the bass boost control. In all cases, this single-band equalizer increases the output of the amplifier around a specific range of frequencies — usually in the 40 to 50 Hz region. What the control doesn’t do is increase the maximum available power from your amp. If your audio system is configured to produce full power with the volume on your radio turned up all the way, turning up the bass boost on an amp or processor will cause the amp to distort at the frequencies that you have boosted. It won’t make the system play any louder.
If you turn the bass boost up 10dB, then you need to turn the gain control by an effective 10dB to keep everything equal. Perhaps it’s easier to leave it alone?
3. Wire the Amplifier To Below-Spec Impedance
 If you have multiple subwoofers with dual voice coil designs, a variety of options are available to wire them to your amp. The voice coils can be wired in series, in a series-parallel configuration or all in parallel. The maximum amount of power an amplifier produces is dependent on the voltage and current provided by the amp. Lower load impedances will typically cause an amp to produce more current and consequently more power. With that said, there is a limit. All amplifiers have a minimum load impedance rating. This means the manufacturer has designed the amp for a specific current limit that won’t over-tax the power supply transformer and the power supply and output switching devices.
If you have multiple subwoofers with dual voice coil designs, a variety of options are available to wire them to your amp. The voice coils can be wired in series, in a series-parallel configuration or all in parallel. The maximum amount of power an amplifier produces is dependent on the voltage and current provided by the amp. Lower load impedances will typically cause an amp to produce more current and consequently more power. With that said, there is a limit. All amplifiers have a minimum load impedance rating. This means the manufacturer has designed the amp for a specific current limit that won’t over-tax the power supply transformer and the power supply and output switching devices.
Changing the way your subs are wired to something that is beyond the specification of your amplifier may allow it to produce a little more power, but in the case of most amplifiers, all it does it make the amp run much hotter because the efficiency is reduced. If your amp was producing 1,000 watts and rewiring it made an extra 50 or even 100 watts, well, that difference is almost inaudible.
4. Adjust the Tone Controls or EQ on Your Radio
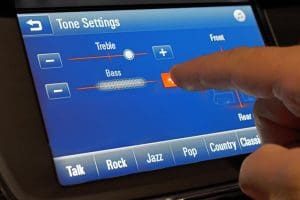 If your radio has an equalizer or simple bass and treble controls, turning them up will make different frequencies of your music louder relative to others. With that said, it won’t make a properly configured and tuned audio system play any louder. Just like the bass boost on an amp, equalizers and tone controls affect the signal level at specific frequencies.
If your radio has an equalizer or simple bass and treble controls, turning them up will make different frequencies of your music louder relative to others. With that said, it won’t make a properly configured and tuned audio system play any louder. Just like the bass boost on an amp, equalizers and tone controls affect the signal level at specific frequencies.
Another common problem with adjusting equalizer controls in a source unit is the ease of distorting the output signal. The preamp signals from radios are rated for a specific amount of voltage, usually 2, 4 or 5 volts RMS. Turning up the tone controls on the deck could cause the signal coming from the radio to distort and make your music sound horrible.
5. Buy the Wrong Amplifier
 All speakers and subwoofers have power ratings. In almost all cases, this rating is the amount of power that the speaker can manage from a thermal standpoint. You see, speakers are notoriously inefficient. More than 95 percent of the energy fed into a speaker is converted to heat. If you feed a woofer 100 watts of power, 95 watts go into heating the voice coil and motor assembly and less than 5 watts are converted into acoustic energy.
All speakers and subwoofers have power ratings. In almost all cases, this rating is the amount of power that the speaker can manage from a thermal standpoint. You see, speakers are notoriously inefficient. More than 95 percent of the energy fed into a speaker is converted to heat. If you feed a woofer 100 watts of power, 95 watts go into heating the voice coil and motor assembly and less than 5 watts are converted into acoustic energy.
If you buy an amplifier that produces more power than a speaker or subwoofer is rated to handle, you will overheat the voice coil assembly, and it will fail.
At the opposite end of the spectrum, having too little power can also cause problems. Let’s say you have a coaxial speaker rated for 70 watts of power and you are using an amplifier rated for 50 watts. You’d think that you are pretty safe, right? If you push that amplifier to the point that its output signal reaches clipping, the amp will produce a great deal more high-frequency energy. The additional energy can cause the tweeter to heat up and possibly fail.
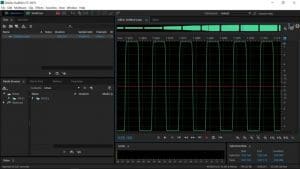 Another consideration about amplifiers is that most can produce 150 percent to 200 percent of their rated power as extra energy when pushed into clipping or distortion. So, a 50-watt amplifier can easily produce 75 watts of distorted power and still damage that 70-watt speaker.
Another consideration about amplifiers is that most can produce 150 percent to 200 percent of their rated power as extra energy when pushed into clipping or distortion. So, a 50-watt amplifier can easily produce 75 watts of distorted power and still damage that 70-watt speaker.
Make sure you have enough power to enjoy your music at the listening levels you want without having to push an amp to the point of distortion.
If you have any questions about purchasing the right products for your mobile audio system, visit your local mobile electronics specialist retailer. They will ensure you get the right solutions that are configured so your car audio system sounds great and will last for years.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.








