We’ve talked about car audio amplifier features and specifications at great length, but up to this point, we haven’t discussed how a car audio amplifier works. In this article, we’ll provide a simple overview of how the power supply in your mobile amplifier can take the 12 volts supplied by your electrical system and convert it into a much higher voltage to drive your speakers.
Making Power for Your Speakers
To supply enough power to your speakers to produce music at realistic listening levels, we need a lot of voltage. For standard 4-ohm speakers, it takes a peak-to-peak voltage of almost 60 volts to deliver about 100 watts to your speaker. In most amplifiers, this voltage is configured as +30V and -30V, relative to the ground reference voltage of your vehicle chassis. So, how in the world do we get plus and minus 30 volts from 12? That’s the job of the power supply.
How a Transformer Works
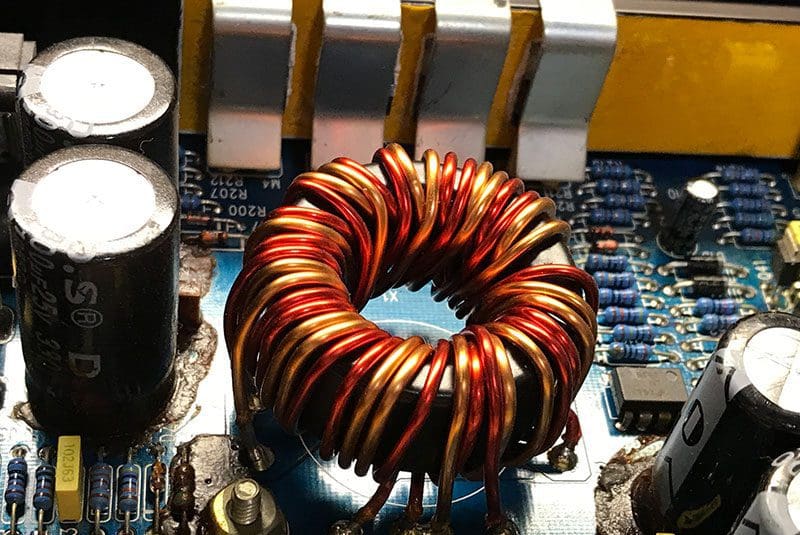
Power supplies couldn’t be created with any reasonable amount of efficiency without a transformer. A transformer is a simple device that increases or decreases alternating current (AC) voltages using two coils of wire wrapped around a magnetically conductive iron core. If you have a 1:2 transformer and feed 12V of AC signal into the primary, you get 24 volts on the output. The big green boxes out on your curb or the cylinders on the power poles near your house are step-down transformers that convert the 16kV feed that enters your neighborhood into 120- and 240-volt feeds to your home.

How Do We Get AC Voltage in a Car?
As you may (or should) know, the power supplied by the battery and alternators in our cars and trucks is direct current (DC). Left in that state and fed into a transformer, we’d see a small voltage spike when the signal was first connected, then nothing. The steady current flowing through the primary winding would simply heat it up and not produce anything on the output side of the transformer.
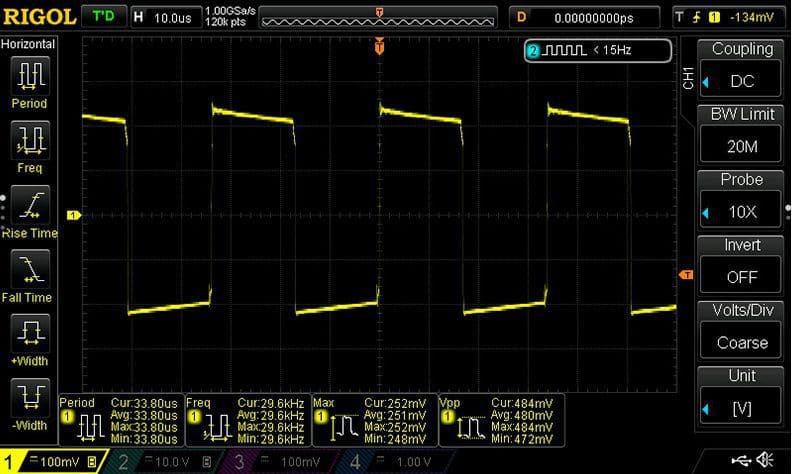
Since we need an AC signal, modern amplifiers use a pulse-width modulator to create a series of square waves that turn on a bank of MOSFETs (electrically controlled high-current switches) that pulse the supply voltage on and off very quickly. Many high-quality amplifiers have power supplies that switch at more than 300kHz.
In the simplest of terms, by switching the connection from the battery to the input of the transformer on and off very quickly, we create an alternating current signal. The voltage of the pulsed signal is increased through the transformer and then fed into a set of diodes and capacitors to smooth it back out to what we call the rail voltage. The rails are the positive and negative power supply sections of the amp that are connected to the output devices.
In application, the circuit is far more complex, but this is the basic operation of the system.
Energy Storage and Power Delivery
As the output voltage of a car audio amp increases, so to does the amount of current flowing to the speaker. The pulse-width modulation controller that manages the power supply can change the relative “on” to “off” time in order to increase the current supplied by the amp. More “on” time means that more current is fed to the transformer, which results in more voltage being produced on the output. Regulated back down to the required rail voltage, this extra voltage ensures that we maintain stable rail voltages.
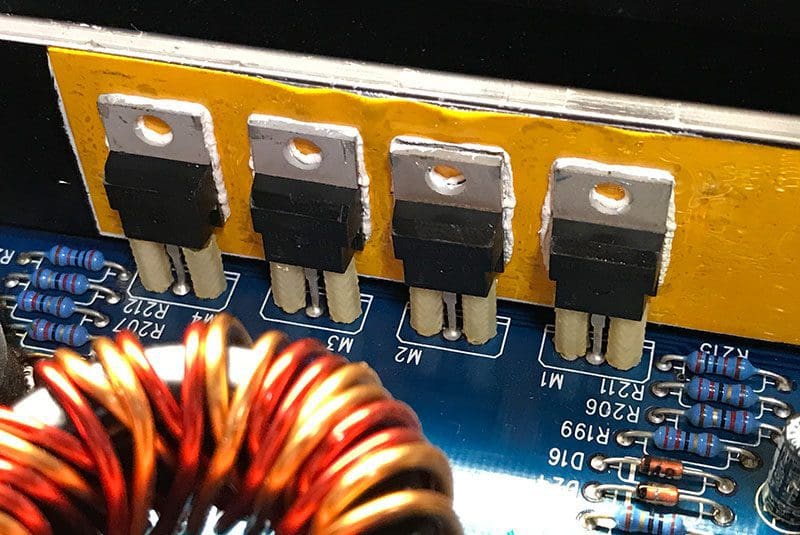
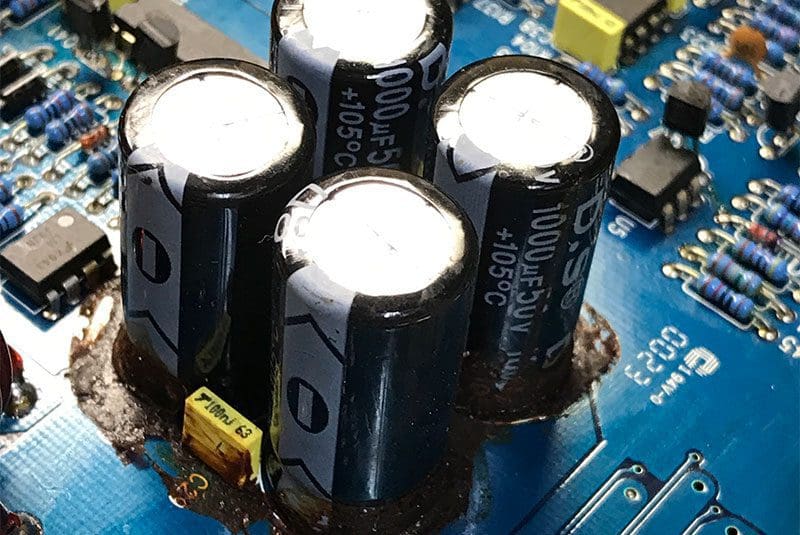
If you look inside an amp, you will almost always see a toroidal transformer and a bank of energy storage capacitors. These large capacitors help smooth the output of the transformer and diode rectifier stage, and store large amounts of energy so that the amp can keep up with the current demands of the audio signal.

Learn How a Car Audio Amplifier Works
You should now have a basic understanding of how your car audio amp converts the 12V feed from your alternator into much higher voltages for the rails. In the next article, we’ll talk about the front end or input stage of a car audio amplifier and discuss crossovers, gain controls and the features and functions that make it easier for your installer to configure your car audio amplifier for optimum performance in your car or truck.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.









